In the rapidly evolving landscape of pharmaceutical regulation, staying ahead of regulatory changes has become more critical than ever. As global drug safety requirements continue to expand and transform, pharmaceutical companies face the monumental challenge of monitoring, interpreting, and responding to regulatory developments across multiple jurisdictions simultaneously.
Enter regulatory intelligence systems – sophisticated platforms that are revolutionizing how pharmaceutical companies approach pharmacovigilance compliance. These systems represent a paradigm shift from reactive compliance management to proactive regulatory strategy, enabling organizations to anticipate changes, adapt quickly, and maintain competitive advantages in an increasingly complex regulatory environment.
In Pharmacovigilance (PV), Regulatory Intelligence involves the collection and analysis of publicly accessible PV regulatory guidelines and regulations, articulating the significance of this information, vigilantly tracking the prevailing regulatory landscape and its impact on company’s current operations. This systematic approach to regulatory monitoring is becoming indispensable for pharmaceutical companies operating in today’s interconnected global marketplace.
This comprehensive guide explores the transformative impact of regulatory intelligence systems on pharmacovigilance operations, examining how these technologies are reshaping drug safety monitoring, compliance management, and strategic decision-making processes across the pharmaceutical industry.
2. Understanding Regulatory Intelligence in Pharmacovigilance
2.1 What Is Regulatory Intelligence?
Regulatory intelligence in pharmacovigilance represents a systematic approach to monitoring, collecting, analyzing, and interpreting regulatory information that impacts drug safety and compliance requirements. Unlike traditional reactive compliance methods, regulatory intelligence systems provide organizations with the tools and insights necessary to anticipate regulatory changes and adapt their pharmacovigilance strategies accordingly.
With insights from regulatory agencies, industry associations, and other key stakeholders, regulatory intelligence is fundamental for staying up to date with the latest developments, patient safety, requirements, compliance, and product quality, according to the ICH Q10 Quality System guideline.
At its core, regulatory intelligence encompasses several key components:
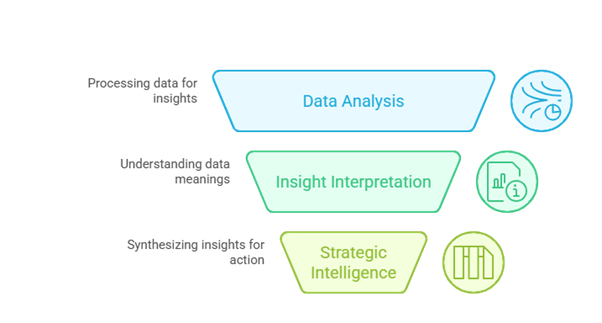
Data Collection and Monitoring:
- Continuous surveillance of regulatory agency websites, publications, and announcements
- Real-time tracking of guideline updates, policy changes, and enforcement actions
- Monitoring of industry publications, conferences, and stakeholder communications
- Analysis of regulatory trends across multiple global jurisdictions
Information Analysis and Interpretation:
- Expert analysis of regulatory changes and their potential business impact
- Assessment of compliance requirements and implementation timelines
- Evaluation of competitive implications and market access considerations
- Risk assessment of regulatory non-compliance scenarios
Strategic Intelligence and Reporting:
- Development of actionable insights for regulatory strategy planning
- Creation of customized reports for different organizational stakeholders
- Establishment of alert systems for critical regulatory developments
- Integration with existing compliance and quality management systems
2.2 The Evolution of Regulatory Intelligence Systems
The pharmaceutical industry has witnessed a remarkable transformation in regulatory intelligence capabilities over the past decade. Traditional manual monitoring processes, which relied heavily on individual expertise and scattered information sources, have given way to sophisticated digital platforms that leverage artificial intelligence, machine learning, and advanced analytics.
Modern regulatory intelligence systems offer several advantages over traditional approaches:
- Comprehensive Coverage: Access to regulatory requirements for over 110 countries, regions, and international organizations through centralized platforms
- Real-Time Updates: Instant access to regulatory insights and real-time updates from national authorities across the globe
- Automated Analysis: Advanced algorithms that can process vast amounts of regulatory information and identify relevant changes
- Predictive Capabilities: AI-powered systems that can anticipate regulatory trends and potential policy changes
- Integration Capabilities: Seamless integration with existing pharmacovigilance systems and workflow processes
3. Core Components and Functionality
3.1 Data Sources and Collection Methods
Modern regulatory intelligence systems draw from an extensive network of information sources to provide comprehensive coverage of the global regulatory landscape. These sources include:
Primary Regulatory Sources:
- FDA guidance documents, warning letters, and policy statements
- EMA guidelines, assessment reports, and safety communications
- Health Canada, TGA, PMDA, and other international regulatory authorities
- ICH guidelines and harmonization initiatives
- Regional regulatory networks and collaborative frameworks
Secondary Information Sources:
- Industry publications and regulatory news services
- Professional associations and standards organizations
- Academic research and regulatory science publications
- Conference proceedings and expert presentations
- Legal and policy analysis reports
Real-Time Monitoring Capabilities:
- Automated web scraping and content analysis
- RSS feeds and notification systems
- Social media monitoring for regulatory discussions
- Patent and intellectual property databases
- Clinical trial registry monitoring
3.2 Advanced Analytics and Intelligence Processing
The true power of regulatory intelligence systems lies in their ability to transform raw regulatory data into actionable business intelligence. Modern systems employ sophisticated analytics capabilities:
Natural Language Processing (NLP):
- Automated extraction of key information from regulatory documents
- Sentiment analysis of regulatory communications
- Multi-language processing for global regulatory coverage
- Classification and categorization of regulatory content
Machine Learning and Predictive Analytics:
- Pattern recognition for identifying regulatory trends
- Predictive modeling for anticipating regulatory changes
- Risk assessment algorithms for compliance impact analysis
- Automated alert generation for critical regulatory developments
Visualization and Reporting Tools:
- Interactive dashboards for regulatory trend monitoring
- Customizable reports for different stakeholder needs
- Timeline visualizations for regulatory change tracking
- Geographic mapping of regulatory requirements
3.3 Integration with Pharmacovigilance Systems
Effective regulatory intelligence systems are designed to integrate seamlessly with existing pharmacovigilance infrastructure, including:
Safety Database Integration:
- Automatic updates to safety reporting requirements
- Real-time synchronization of regulatory timelines
- Integration with case processing workflows
- Automated compliance checking and validation
Quality Management System Integration:
- Incorporation into change control processes
- Integration with training and competency systems
- Alignment with audit and inspection preparation
- Connection to corrective and preventive action (CAPA) systems
Regulatory Submission Systems:
- Automated updates to submission templates and requirements
- Integration with regulatory correspondence tracking
- Alignment with regulatory milestone planning
- Connection to regulatory intelligence databases
4. Real-World Applications and Use Cases
4.1 Proactive Compliance Management (h4)
Regulatory intelligence systems enable pharmaceutical companies to move from reactive compliance management to proactive regulatory strategy. Real-world applications include:
Regulatory Change Impact Assessment: A global pharmaceutical company uses regulatory intelligence to monitor FDA guidance updates related to periodic safety reports. When the agency announces changes to PSUR submission requirements, the system automatically:
- Identifies affected products and therapeutic areas
- Assesses the impact on existing submission timelines
- Generates alerts for relevant stakeholders
- Provides recommended action plans for compliance
Multi-Jurisdictional Compliance Monitoring: Regulatory Intelligence is a critical tool for pharmacovigilance, as it can help identify new safety concerns and keep track of emerging trends. It can also help assess the impact of regulatory changes on a company’s product portfolio. For example, when the European Union updates its pharmacovigilance legislation, companies can immediately assess the impact across their entire European product portfolio and develop coordinated compliance strategies.
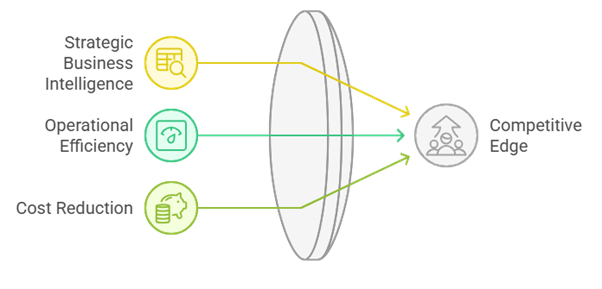
4.2 Strategic Business Intelligence
Beyond compliance management, regulatory intelligence systems provide valuable strategic insights for business decision-making:
Market Access Planning:
- Early identification of regulatory pathways for new products
- Assessment of competitive regulatory advantages
- Evaluation of regulatory barriers to market entry
- Analysis of regulatory requirements for different therapeutic areas
Risk Management and Mitigation:
- Early warning systems for regulatory enforcement actions
- Analysis of regulatory trends that could impact product safety profiles
- Assessment of regulatory risks in merger and acquisition activities
- Evaluation of regulatory implications for clinical trial design
Competitive Intelligence:
- Monitoring of competitor regulatory activities and submissions
- Analysis of regulatory approval timelines and success rates
- Assessment of regulatory strategy effectiveness
- Identification of regulatory opportunities and threats
4.3 Operational Efficiency and Cost Reduction
Regulatory intelligence systems deliver significant operational benefits through automation and standardization:
Resource Optimization:
- Reduction in manual regulatory monitoring activities
- Elimination of duplicate regulatory research efforts
- Streamlined regulatory intelligence reporting processes
- Improved efficiency in regulatory strategy development
Cost Reduction:
- Decreased regulatory consulting and external monitoring costs
- Reduced compliance-related penalties and enforcement actions
- Minimized delays in regulatory submission processes
- Optimized resource allocation for regulatory activities
5. Benefits and Impact on Pharmacovigilance Operations
5.1 Enhanced Regulatory Compliance
The implementation of regulatory intelligence systems has demonstrated significant improvements in compliance outcomes across the pharmaceutical industry:
Improved Compliance Rates: Organizations using regulatory intelligence systems report 40-60% reduction in compliance-related issues and regulatory citations. This improvement stems from:
- Early identification of regulatory changes before implementation deadlines
- Automated compliance checking and validation processes
- Standardized interpretation of regulatory requirements
- Proactive remediation of potential compliance gaps
Reduced Regulatory Risk:
- Decreased likelihood of regulatory enforcement actions
- Improved preparation for regulatory inspections and audits
- Enhanced ability to demonstrate regulatory compliance
- Reduced legal and financial risks associated with non-compliance
5.2 Operational Efficiency Gains
Time Savings:
- 70-80% reduction in time spent on manual regulatory monitoring activities
- Faster regulatory change impact assessment and response
- Streamlined regulatory intelligence reporting processes
- Accelerated regulatory strategy development and implementation
Resource Optimization:
- Reallocation of regulatory professionals to higher-value strategic activities
- Reduced dependency on external regulatory consulting services
- Improved cross-functional collaboration on regulatory matters
- Enhanced utilization of regulatory expertise across the organization
5.3 Strategic Competitive Advantages
Market Access Acceleration:
- Earlier identification of regulatory opportunities for new products
- Improved regulatory pathway selection and optimization
- Enhanced ability to anticipate and respond to regulatory changes
- Faster adaptation to evolving regulatory requirements
Innovation Support:
- Better understanding of regulatory requirements for emerging technologies
- Improved regulatory strategy for novel therapeutic approaches
- Enhanced ability to engage with regulatory authorities on innovative products
- Reduced regulatory uncertainty for research and development activities
5.4 Data-Driven Decision Making
Modern regulatory intelligence systems provide pharmaceutical companies with unprecedented access to regulatory data and analytics:
Quantitative Analysis:
- Trend analysis of regulatory approval timelines and success rates
- Comparative analysis of regulatory requirements across jurisdictions
- Risk assessment modeling for regulatory compliance scenarios
- Performance metrics for regulatory strategy effectiveness
Predictive Insights:
- Forecasting of regulatory changes and their potential impact
- Identification of emerging regulatory trends and patterns
- Predictive modeling for regulatory approval probabilities
- Early warning systems for regulatory enforcement activities
6. Implementation Challenges and Solutions
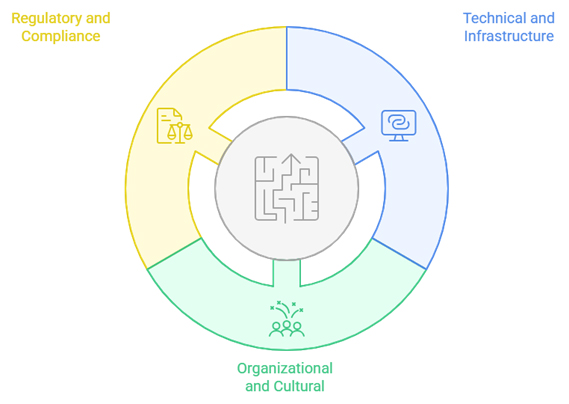
6.1 Technical and Infrastructure Challenges
Data Integration Complexity: Implementing regulatory intelligence systems often requires integration with existing pharmacovigilance infrastructure, which can present technical challenges:
Solutions:
- Phased implementation approach with gradual system integration
- Use of standardized APIs and data exchange protocols
- Investment in middleware solutions for system connectivity
- Collaboration with technology vendors for customized integration solutions
Data Quality and Standardization: Regulatory information comes from diverse sources with varying data formats and quality standards:
Solutions:
- Implementation of data validation and cleansing processes
- Development of standardized regulatory data taxonomies
- Use of natural language processing for data standardization
- Establishment of data quality monitoring and improvement processes
6.2 Organizational and Cultural Challenges
Change Management: Transitioning from traditional regulatory monitoring to automated intelligence systems requires significant organizational change:
Solutions:
- Comprehensive change management programs with stakeholder engagement
- Training and competency development for regulatory professionals
- Clear communication of benefits and expectations
- Gradual transition with parallel operation periods
Skills and Competency Development: Regulatory intelligence systems require new skills and competencies from regulatory professionals:
Solutions:
- Investment in training programs for regulatory intelligence tools
- Development of new job roles and career paths
- Collaboration with external training providers and consultants
- Creation of internal centers of excellence for regulatory intelligence
6.3 Regulatory and Compliance Considerations
Validation and Qualification: Regulatory intelligence systems must be validated and qualified according to pharmaceutical quality standards:
Solutions:
- Development of comprehensive validation protocols
- Documentation of system capabilities and limitations
- Regular system performance monitoring and validation
- Compliance with applicable regulatory guidelines and standards
Data Security and Privacy: Regulatory intelligence systems handle sensitive regulatory and business information:
Solutions:
- Implementation of robust cybersecurity measures
- Compliance with data protection regulations
- Establishment of data access controls and audit trails
- Regular security assessments and penetration testing
7. Future Outlook and Emerging Trends
7.1 Technological Advancement and Innovation
The future of regulatory intelligence systems in pharmacovigilance will be shaped by several key technological trends:
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: The impact of cutting-edge technologies like artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning on drug development and pharmacovigilance continues to expand. Future systems will feature:
- Advanced natural language processing for regulatory document analysis
- Predictive modeling for regulatory change forecasting
- Automated regulatory strategy optimization
- Intelligent alert systems with reduced false positives
Integration with Emerging Technologies:
- Blockchain technology for regulatory data integrity and traceability
- Internet of Things (IoT) integration for real-time regulatory monitoring
- Cloud-based platforms for global regulatory intelligence sharing
- Mobile applications for on-the-go regulatory intelligence access
Enhanced Analytics and Visualization:
- Real-time regulatory dashboard and reporting capabilities
- Advanced data visualization tools for regulatory trend analysis
- Interactive regulatory intelligence platforms for stakeholder engagement
- Customizable analytics for different organizational needs
7.2 Regulatory Evolution and Harmonization
Global Regulatory Harmonization:
- Increased standardization of regulatory requirements across jurisdictions
- Development of common regulatory intelligence standards and protocols
- Enhanced international cooperation on regulatory intelligence sharing
- Streamlined regulatory processes for global pharmaceutical companies
Regulatory Science Advancement:
- Integration of real-world evidence into regulatory intelligence systems
- Enhanced focus on patient-centered regulatory approaches
- Development of regulatory intelligence for personalized medicine
- Improved understanding of regulatory decision-making processes
7.3 Industry Transformation and Adaptation
Collaborative Intelligence Networks:
- Industry-wide regulatory intelligence sharing platforms
- Collaborative approaches to regulatory monitoring and analysis
- Shared regulatory intelligence databases and resources
- Joint industry initiatives for regulatory intelligence advancement
Sustainable Regulatory Intelligence:
- Focus on environmental sustainability in regulatory intelligence operations
- Development of cost-effective regulatory intelligence solutions
- Emphasis on regulatory intelligence accessibility for smaller companies
- Integration of sustainability considerations into regulatory strategy
8. Conclusion
In today’s highly dynamic and globalized regulatory environment, regulatory intelligence systems have evolved from a competitive advantage to an operational necessity. These systems empower pharmacovigilance teams to move beyond reactive compliance toward a more predictive, proactive, and strategic approach to regulatory management.
By harnessing advanced technologies such as AI, machine learning, and NLP, pharmaceutical companies can streamline regulatory monitoring, reduce compliance risks, and respond faster to emerging safety requirements. Moreover, integrating regulatory intelligence into broader pharmacovigilance operations enhances decision-making, accelerates market access, and supports innovation in drug safety.



