
The pharmaceutical industry stands at a pivotal moment in drug safety monitoring. As we advance through 2025, artificial intelligence is fundamentally transforming how we detect, analyze, and respond to adverse drug reactions. For pharmaceutical professionals, understanding this shift from traditional pharmacovigilance methods to AI-powered systems isn’t just beneficial—it’s essential for staying competitive and ensuring patient safety.
This transformation affects every aspect of drug safety monitoring, from the speed of signal detection to the quality of regulatory reporting. Whether you’re a seasoned pharmacovigilance professional or a pharmaceutical executive looking to modernize your safety operations, this guide will help you understand what’s changing and why it matters.
Traditional pharmacovigilance has served as the backbone of drug safety for decades. This established system relies on structured processes where healthcare professionals, patients, and pharmaceutical companies report adverse events through standardized forms and databases. The process typically involves manual review of case reports, literature searches, and periodic safety updates.
Key Components of Traditional Systems
The traditional approach centers around several core elements:
● Spontaneous reporting systems where adverse events are manually documented
● Literature reviews conducted by safety professionals
● Periodic safety update reports (PSURs) compiled through manual data analysis
● Signal detection performed by experienced pharmacovigilance officers
Strengths That Built the Industry
Traditional pharmacovigilance established crucial foundations that continue to influence modern practices. The human expertise involved in case evaluation ensures nuanced understanding of complex medical situations. Regulatory frameworks developed around these methods provide clear guidelines and standardized processes that have protected patients for generations.
Volume and Complexity Overload
Modern pharmaceutical companies face an unprecedented influx of safety data. A single blockbuster drug can generate hundreds of thousands of adverse event reports annually. Traditional manual processing methods struggle to keep pace with this volume, creating bottlenecks that can delay critical safety signals.
Resource Intensity
Traditional pharmacovigilance requires substantial human resources. Skilled safety professionals must manually review each case, conduct literature searches, and prepare regulatory reports. This labor-intensive approach becomes increasingly expensive as data volumes grow.
Detection Delays
Manual signal detection processes can take weeks or months to identify potential safety concerns. In an era where social media and digital health platforms generate real-time safety information, these delays can impact patient safety and regulatory compliance.
Artificial intelligence in pharmacovigilance encompasses several key technologies working together to enhance drug safety monitoring. Machine learning algorithms can process vast amounts of unstructured data, while natural language processing enables systems to understand and analyze text-based reports from multiple sources.
Machine Learning Applications
Machine learning models excel at pattern recognition within large datasets. These systems can identify subtle correlations between drug exposures and adverse events that might escape human detection. Advanced algorithms continuously improve their accuracy as they process more data, creating increasingly sophisticated safety monitoring capabilities.
Natural Language Processing Breakthroughs
Modern NLP systems can extract meaningful information from various text sources, including social media posts, electronic health records, and medical literature. This capability dramatically expands the scope of safety monitoring beyond traditional reporting channels.
Industry Adoption Patterns
Leading pharmaceutical companies are implementing AI solutions across different aspects of their safety operations. Early adopters focus on automating routine tasks like case processing and literature monitoring, while more advanced implementations include predictive safety modeling and real-time signal detection.
Regulatory Acceptance
Regulatory agencies worldwide are increasingly accepting AI-enhanced pharmacovigilance processes. The FDA and EMA have published guidelines for AI implementation in drug safety, providing frameworks for validation and compliance.
Real-Time Processing Capabilities
AI systems can process safety data in real-time, analyzing adverse event reports as they arrive rather than waiting for batch processing. This immediate analysis enables faster signal detection and more timely safety responses.
Traditional methods might require days or weeks to process a complex case report, while AI systems can analyze thousands of reports simultaneously within minutes. This speed advantage becomes crucial during safety crises where rapid response can protect patient welfare.
Automated Literature Monitoring
AI-powered systems continuously scan medical literature, regulatory databases, and social media platforms for safety signals. This automated monitoring provides comprehensive coverage that would be impossible to achieve manually.
Pattern Recognition Superiority
AI algorithms excel at identifying complex patterns across multiple data sources. These systems can detect subtle correlations that human reviewers might miss, particularly when analyzing large datasets with multiple variables.
Predictive Analytics Integration
Advanced AI systems don’t just detect existing safety signals—they predict potential future risks based on historical patterns and emerging data trends. This predictive capability enables proactive safety management rather than reactive responses.
Global Data Integration
AI systems can simultaneously analyze safety data from multiple countries, languages, and data sources. This global perspective provides more comprehensive safety monitoring than traditional region-specific approaches.
Comprehensive Source Monitoring
Modern AI implementations monitor traditional reporting channels alongside social media, electronic health records, insurance claims, and wearable device data. This multi-source approach creates a more complete picture of drug safety profiles.
Operational Efficiency Gains
AI implementation delivers significant operational improvements across pharmacovigilance operations:
● Reduced processing time from weeks to hours for complex safety assessments
● Lower operational costs through automation of routine tasks
● Improved resource allocation allowing human experts to focus on complex cases requiring clinical judgment
● Enhanced consistency in case evaluation and signal detection
Enhanced Safety Monitoring
AI systems provide superior safety monitoring capabilities through:
● Earlier signal detection identifying potential safety issues before they become widespread
● Improved signal quality reducing false positives while capturing true safety signals
● Comprehensive coverage monitoring multiple data sources simultaneously
● Predictive insights enabling proactive safety management
Technical Complexity
Implementing AI in pharmacovigilance requires significant technical expertise and infrastructure investment. Organizations must develop or acquire sophisticated systems capable of handling complex medical data while maintaining regulatory compliance.
Data Quality Requirements
AI systems require high-quality, structured data to function effectively. Many pharmaceutical companies face challenges in cleaning and standardizing their historical safety data for AI processing.
Regulatory Compliance Considerations
While regulatory acceptance is growing, companies must navigate complex compliance requirements when implementing AI systems. Validation procedures, audit trails, and explainable AI requirements add complexity to implementation efforts.
Human Expertise Integration
Successfully implementing AI requires careful integration with existing human expertise. Organizations must determine optimal workflows that leverage AI capabilities while maintaining appropriate human oversight and clinical judgment.
Validation and Testing Protocols
Comprehensive validation procedures ensure AI systems meet regulatory requirements and perform reliably in production environments. These protocols include accuracy testing, bias detection, and performance monitoring systems.
Change Management Approaches
Successful AI implementation requires careful change management to help safety professionals adapt to new workflows and technologies. Training programs and gradual implementation strategies help minimize disruption while maximizing benefits.
Advanced AI Capabilities
The next generation of AI pharmacovigilance systems will incorporate more sophisticated technologies:
● Deep learning models that can understand complex medical relationships
● Multimodal AI systems that process text, images, and structured data simultaneously
● Federated learning approaches that enable collaboration while maintaining data privacy
● Explainable AI systems that provide clear reasoning for safety decisions
Integration with Digital Health
AI pharmacovigilance systems are increasingly integrating with digital health platforms, wearable devices, and electronic health records. This integration creates comprehensive safety monitoring ecosystems that capture real-world evidence more effectively than traditional approaches.
Harmonized Standards
International regulatory bodies are working toward harmonized standards for AI in pharmacovigilance. These standards will facilitate global implementation while ensuring consistent safety monitoring across different jurisdictions.
Advanced Analytics Acceptance
Regulatory agencies are becoming more accepting of advanced analytics and AI-generated insights in safety reporting. This acceptance will accelerate adoption and enable more innovative approaches to drug safety monitoring.
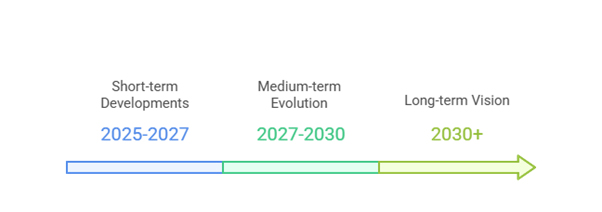
Short-term Developments (2025-2027)
● Widespread adoption of AI-assisted case processing and literature monitoring
● Improved integration between AI systems and existing pharmacovigilance workflows
● Enhanced regulatory guidance for AI implementation in drug safety
Medium-term Evolution (2027-2030)
● Predictive safety modeling becoming standard practice
● Real-time global safety monitoring networks
● AI-powered personalized safety assessments based on patient characteristics
Long-term Vision (2030+)
● Fully integrated AI pharmacovigilance ecosystems
● Proactive safety management preventing adverse events before they occur
● Personalized medicine safety monitoring tailored to individual patient profiles
The transformation from traditional pharmacovigilance to AI-powered safety monitoring represents one of the most significant advances in pharmaceutical safety management. As we progress through 2025, the benefits of AI implementation—including faster signal detection, improved efficiency, and enhanced patient safety—are becoming increasingly clear.
However, successful transformation requires careful planning, appropriate investment, and thoughtful integration of AI capabilities with existing expertise. Organizations that embrace this change while maintaining focus on regulatory compliance and patient safety will be best positioned to thrive in the evolving pharmaceutical landscape.
The future of pharmacovigilance lies not in replacing human expertise but in augmenting it with powerful AI capabilities. By understanding both the opportunities and challenges of this transformation, pharmaceutical professionals can make informed decisions about implementing AI solutions that enhance drug safety monitoring while maintaining the highest standards of patient protection.